- How to create Database in ASP.NET Core?
- Store Connection String in appsettings.json file
- How to retrieve connection string from appsettings.json file?
- Make model class to save data to database
Till now, you have learned how to make a model class in asp.net core and how to connect it with the controller. In this chapter, you will learn the whole package including creating a model and saving data to the database. This chapter is going to be quite interesting because once you complete this chapter you will be able to apply your own logic to database and project. So, study this chapter thoroughly to understand the basic concept of working with the database in ASP.NET Core.
Here, I am creating a New Project UserProfile, that will ask user details and save into database.
Create Your First ASP.NET Core Project
Design View Page
@{
ViewBag.Title = "User Profile";
}
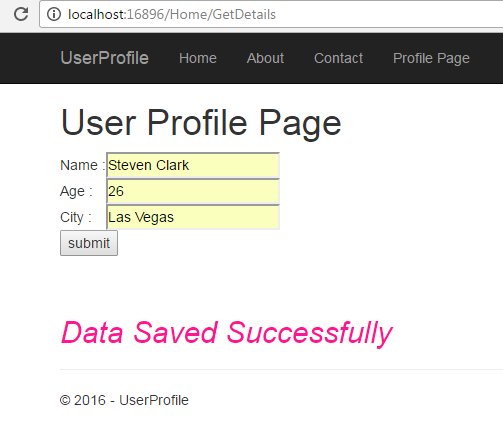
<h1>User Profile Page</h1>
<form asp-controller="Home" asp-action="GetDetails" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Name :</td>
<td><input name="txtName" type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Age :</td>
<td><input name="txtAge" type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>City :</td>
<td><input name="txtCity" type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><input id="Submit1" type="submit" value="submit" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<br /><br />
<h2 style="font-style:italic; color:deeppink">@ViewBag.Result</h2>
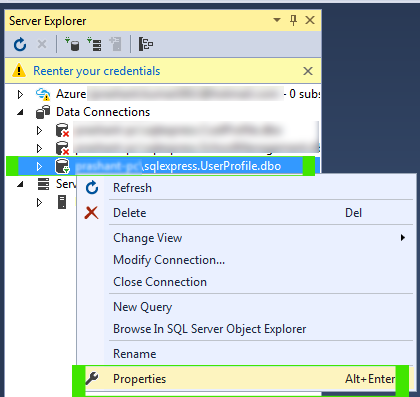
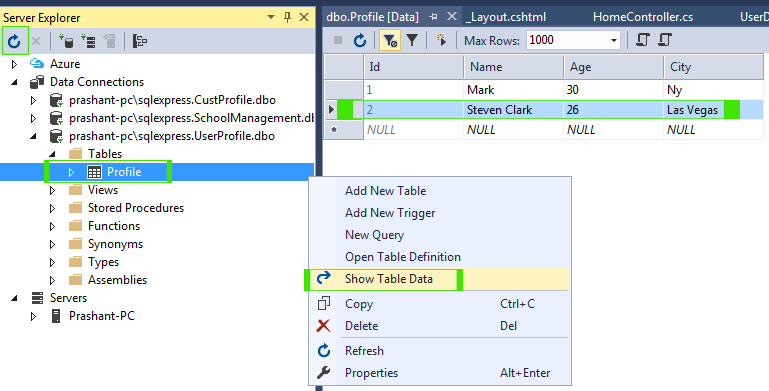
Create Database and Table
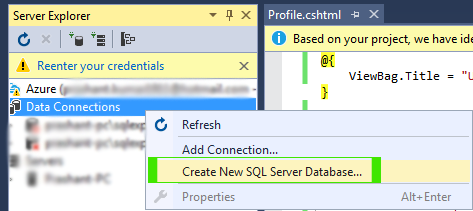
.\SQLEXPRESS as Server Name and UserProfile as Database Name as picture below. 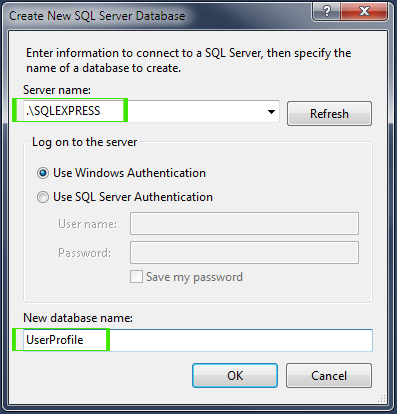
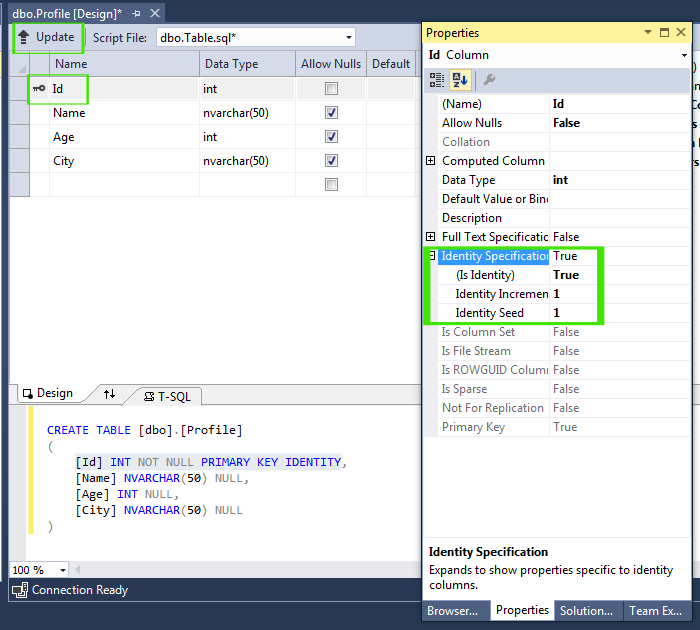
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Profile]
(
[Id] INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY,
[Name] NVARCHAR(50) NULL,
[Age] INT NULL,
[City] NVARCHAR(50) NULL
)
Get Connection String
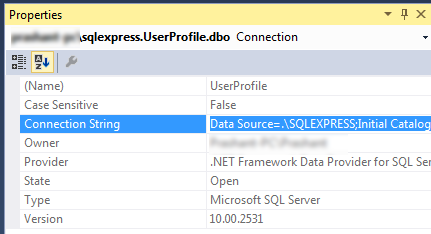
Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=UserProfile;Integrated Security=True;Pooling=False
appsettings.json file. Add your Connection Strings using following method.
{
"Logging": {
"IncludeScopes": false,
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Debug",
"System": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Information"
}
},
ConnectionStrings": {
"UserProfile": "Data Source=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=UserProfile;Integrated Security=True;Pooling=False"
}
}
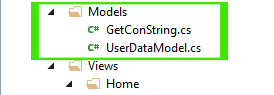
Now, I will make a class in models folder that will access this connection strings when needed.
Creating Models Folder and Class
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using System.IO;
namespace UserProfile.Models
{
public static class GetConString
{
public static string ConString()
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder().SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()).AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true);
var config = builder.Build();
string constring = config.GetConnectionString("UserProfile");
return constring;
}
}
}
This class file will return Connection String that will be used to connecting with your database.
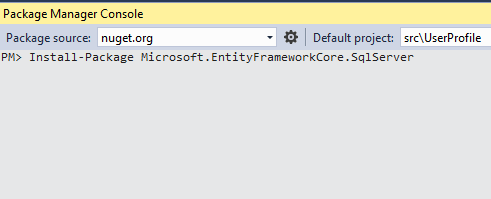
Installing Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer is Necessary
You must install Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer to work with Sql Data Client. It is very easy to install. Go to Tools NuGet Package Manager Package Manager Console. Here, type the following command and Hit Enter. Package will be automatically installed and restored on your project within couple of seconds.
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace UserProfile.Models
{
public class UserDataModel
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public int SaveDetails()
{
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(GetConString.ConString());
string query = "INSERT INTO Profile(Name, Age, City) values ('" + Name + "','" + Age + "','" + City + "')";
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(query, con);
con.Open();
int i = cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
return i;
}
}
}
using System; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using UserProfile.Models; namespace UserProfile.Controllers { public class HomeController : Controller { public IActionResult Index() { return View(); } public IActionResult About() { ViewData["Message"] = "Your application description page."; return View(); } public IActionResult Contact() { ViewData["Message"] = "Your contact page."; return View(); } public IActionResult Error() { return View(); } public IActionResult Profile() { return View(); } [HttpPost] public IActionResult GetDetails() { UserDataModel umodel = new UserDataModel(); umodel.Name = HttpContext.Request.Form["txtName"].ToString(); umodel.Age = Convert.ToInt32(HttpContext.Request.Form["txtAge"]); umodel.City = HttpContext.Request.Form["txtCity"].ToString(); int result = umodel.SaveDetails(); if(result>0) { ViewBag.Result = "Data Saved Successfully"; } else { ViewBag.Result = "Something Went Wrong"; } return View("Profile"); } } }
<div class="navbar-collapse collapse">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">Home</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="About">About</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Profile">Profile Page</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
Summary
This chapter explains complete guide of MVC. Here, you learned how to design a form in View, How to write code in the controller, how to create a model class file and save data to the database. It is just a demo and you will learn more in next chapter.